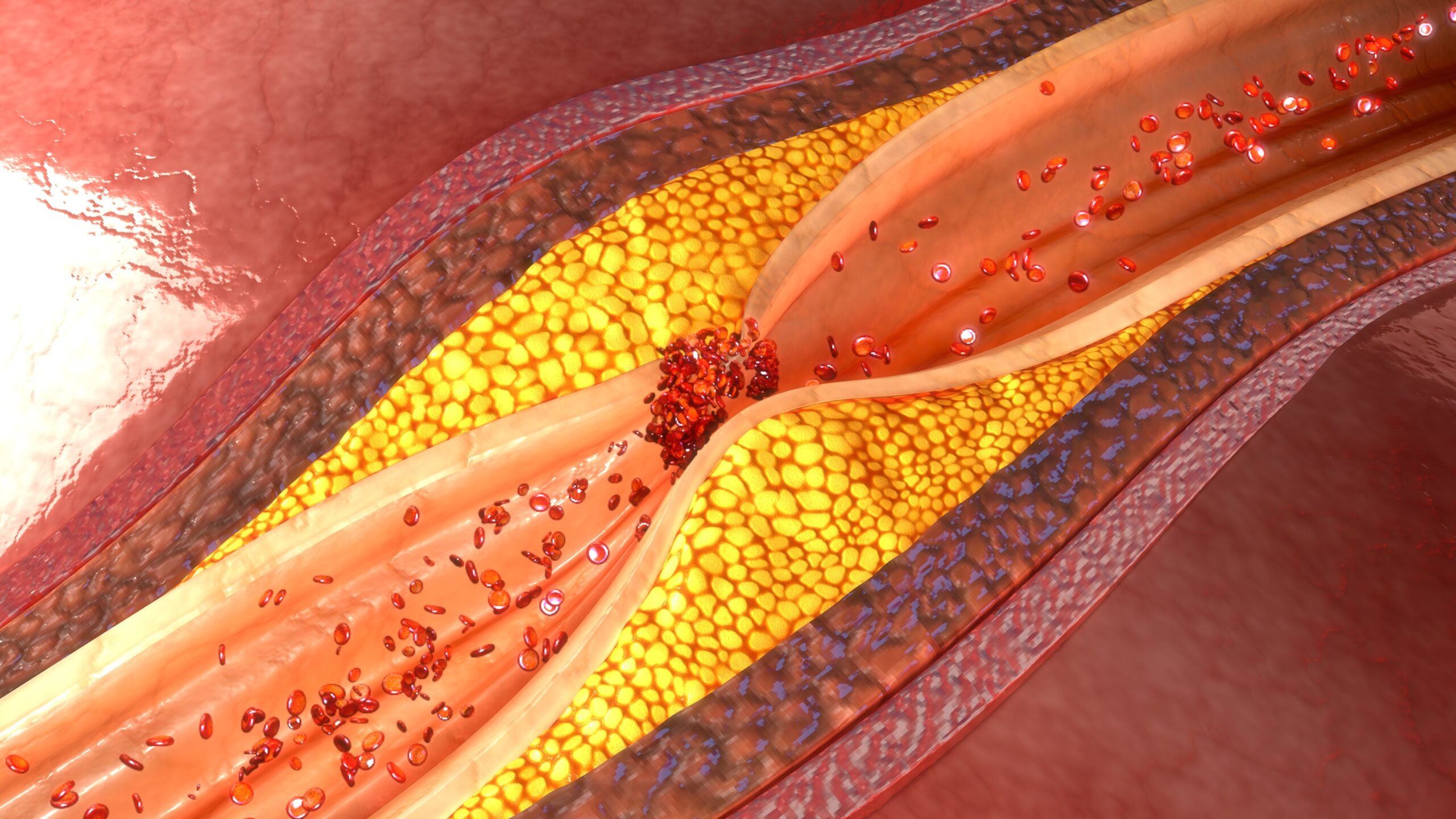
According to the CDC, around 94 million Americans above the age of 20 have cholesterol levels above 200 mg/dL (normal cholesterol levels are less than 200mg/dL). Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance that the body uses to produce vitamin D, hormones, and bile, a fluid needed for digestion. The body naturally produces cholesterol, but it is also found in the food we eat from animal sources.
Cholesterol can only travel through the blood vessels on particles made of protein and fats called lipoproteins, including low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and high-density lipoproteins (HDL). LDL is most commonly referred to as “bad” cholesterol because high levels of LDL cause buildup in the arteries, while HDL is referred to as “healthy” cholesterol because it brings cholesterol to the liver to be filtered out from the body.
The build-up of LDL deposits on the arterial walls, referred to as “plaque,” decreases the amount of oxygen and nutrients able to flow through the arteries. This can lead to coronary heart disease, angina (chest pain from decreased blood flow to the heart), and chronic kidney disease, amongst other chronic conditions. Furthermore, a piece of plaque can break off and get stuck in an artery, causing a stroke or a heart attack.
It is important to treat high cholesterol with proper diet, exercise, and medication. One such medication that is commonly prescribed by doctors is atorvastatin, the generic form of the brand name medication Lipitor®.
Atorvastatin can be an effective way to manage high cholesterol.
Image Source: MStudioImages
Atorvastatin is an “HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor”. Cholesterol is made in the liver and HMG-CoA reductase is an enzyme that controls how much cholesterol can be made. In theory, by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, atorvastatin reduces the amount of cholesterol made in the liver. A review done by Malhoutra et al. showed that 10-80 mg/day of atorvastatin reduces LDL, triglyceride, and VLDL (very low-density lipoprotein) levels while increasing HDL levels in patients with high cholesterol.
Unfortunately, these benefits come with some downsides as well. Some common side effects of atorvastatin include headaches, lower back/side pain, pain around the eyes and cheekbones, painful or difficult urination, and stuffy or runny noses. Atorvastatin also has drug interactions with Paxlovid, several HIV medications, and even other kinds of cholesterol medication. Another complication is that grapefruit juice should not be consumed while taking atorvastatin because it interferes with the breakdown of the drug in the intestines.
Despite the side effects mentioned, atorvastatin, along with proper diet and exercise, is an effective and safe option for those with high cholesterol. As with all medications, a medical professional should always be consulted for any questions or concerns.
Featured Image Source: 7activestudio