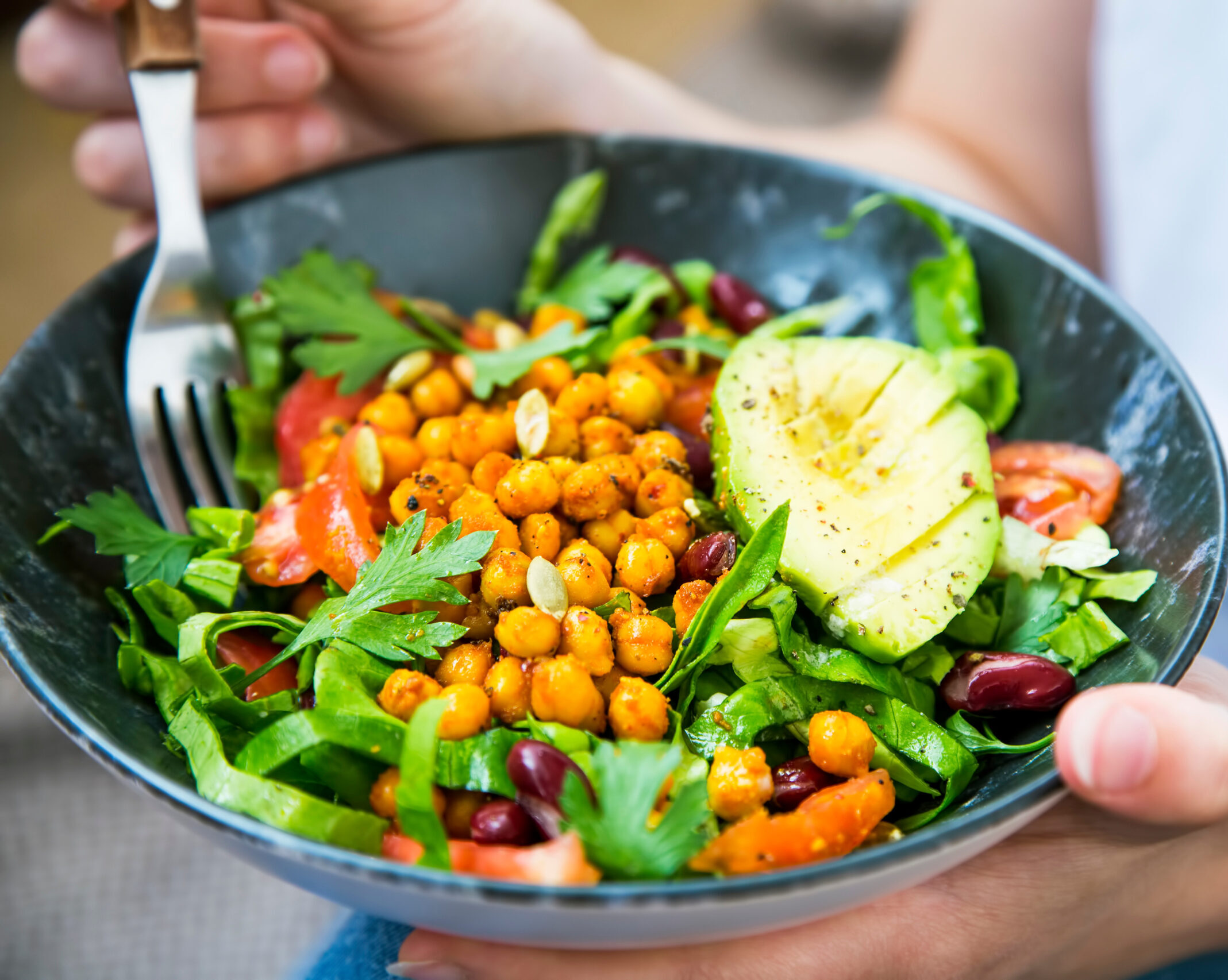About 15% of human-caused greenhouse gases come from livestock farming, and close to half of the world’s grain goes to feeding animals for slaughter. Environmental concerns are one rising reason for people to switch to a more plant-based diet, but even with values aside, they have serious health benefits that can make an optimal diet. Simply replacing meat with plant-based meats has many benefits such as decreasing inflammation and cholesterol, reducing the risk of hypertension, cardiovascular disease, cancer and saturated fat intake, improving blood sugar and weight stability, bowel regularity, and gut health.
Relying primarily on fruits, vegetables, lentils, whole proteins such as tofu, and grains or just reducing meat consumption has significant health benefits. For example, the higher amount of antioxidants and minerals in plant-based diets can help lower blood pressure, causing a 75% decrease in risk of hypertension compared to omnivores. Cardiovascular health also improves with this diet, as well as digestive, immune, and blood sugar health. However, since the plant-based lifestyle has grown more popular, plant-based junk food and imitation meats can give a bad name for plant-based foods, both of which can come with health concerns of their own.
For instance, one concern many people have is protein content; fortunately, this can actually be comparable in plant-based diets, depending on the what is being compared. For instance, plant-based chicken is particularly close to the protein content of natural chicken. Similarly, the cholesterol content of plant-based meat is negligible leading to a reduction of heart diseases. Natural meat also has a higher accumulation of environmental toxins and microbial contamination that can have fatal results, artificially injected hormones that can cause hormonal imbalance and impotence, and meat is even now being called carcinogenic.
Plant-based meat options can be comparable in nutrition, appearance, and taste.
Image Source: Rocky89
However, despite these many benefits listed, plant-based meats cannot just be consumed with no care in the world. While meat products can have high sodium content, plant-based meat is not immune to this as many often have beyond the recommended amount as well. Vitamin B12 is an important nutrient essential in nerve function and red blood cell formation among other things, and it is often missing in plant-based diets. Similarly, iron and zinc may be lower in a plant-based diet. Fortunately, lots of plant based meat is fortified with B12, iron and zinc additives, and there are many commercially available supplements.
Overall, while a vegetarian diet brings about many health benefits and while plant-based alternatives to meat are overall preferable if the missing nutrients are supplemented, we all still have to watch what we eat. Prioritizing whole foods and protein sources, such as tofu, tempeh, lentils, and nuts, as well as watching sugar and sodium intake are essential to any person’s health. That being said, there is little to lose and much to gain by simply reducing meat consumption.
Featured Image: © marrakeshh / Adobe Stock